How to Answer the AP English Language and Composition Essay Questions
April 7, 2024

Answering the AP English Language and Composition Synthesis Essay Question
Sample Synthesis Essay Question
SUGGESTED TIME:
15 MINUTES FOR READING THE QUESTION AND SOURCES
40 MINUTES FOR WRITING AN ESSAY
Homework has always been part of going to school. In recent years, efforts to improve education have included assigning more homework to students from kindergarten to twelfth grade. Many teachers, parents, and others applaud this increase. Critics, in contrast, claim that heavier loads of homework do more harm than good, not only to children but also to their families.
Carefully read the following six sources, including the material that introduces each source. Then, in an essay that synthesizes at least three of the sources, take a position on the claim that large amounts of homework have more negative consequences than positive ones.
Source A (Kohn)
Source B (Gill and Schlossman)
Source C (Loveless)
Source D (Chart)
Source E (Haley)
Source F (Chaika)
Source G (Hanson)
Instructions:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that may establish a line of reasoning.
- Provide evidence from at least three of the provided sources to support the thesis. Indicate clearly the sources used through direct quotation, paraphrase, or summary. Sources may be cited as Source A, Source B, etc., or by using the descriptions in parentheses.
- Explain the relationship between the evidence and the thesis.
- Demonstrate an understanding of the rhetorical situation.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating the argument.
Sources
SOURCE A
Alfie Kohn, “Homework: An Unnecessary Evil?” Psychology Today, published online at www.psychologytoday.com, November 24, 2012.
The following passage is an excerpt from an article written by an author and specialist in behavior and education. His books include The Homework Myth and What Does It Mean to Be Well Educated?
At the high school level, the research supporting homework hasn’t been particularly persuasive. There does seem to be a correlation between homework and standardized test scores, but (a) it isn’t strong, meaning that homework doesn’t explain much of the variance in scores, and (b) one prominent researcher, Timothy Keith, who did find a solid correlation, returned to the topic a decade later to enter more variables into the equation simultaneously, only to discover that the improved study showed that homework had no effect after all.
. . . When homework is related to test scores, the connection tends to be strongest—or, actually, least tenuous—with math. If homework turns out to be unnecessary for students to succeed in that subject, it’s probably unnecessary everywhere.
Along comes a new study, then, that focuses on the neighborhood where you’d be most likely to find a positive effect if one was there to be found: the effect of math and science homework on grades in high school . . . .
This result clearly caught the researchers off-guard. Frankly, it surprised me, too. When you measure “achievement” in terms of grades, you expect to see a positive result—not because homework is academically beneficial but because the same teacher who gives the assignments evaluates the students who complete them, and the final grade is often based at least partly on whether, and to what extent, students did the homework.
It’s important to remember that some people object to homework for reasons that aren’t related to the dispute about whether research might show that homework provides academic benefits. They argue that (a) six hours a day of academics are enough, and kids should have the chance after school to explore other interests and develop in other ways—or be able simply to relax in the same way that most adults like to relax after work; and (b) the decision about what kids do during family time should be made by families, not schools.
SOURCE B
Brian P. Gill and Steven L. Schlossman, “My Dog Ate My Argument,” Op/Ed page of the Los Angeles Times, December 11, 2003.
The following passage is an excerpt from an opinion article written by a social scientist at the RAND Corporation and a history professor at Carnegie Mellon University.
In our view, homework is the prime window into the school for parents to see, understand and connect with the academic mission of the teachers. It is the primary arena in which children, parents and schools interact on a daily basis. Yet it gets less systematic thought and attention than any other key component of education. Other than the admonition that kids should do more of it, we pay almost no attention to how to improve its design and content. Nor do we do much to prepare teachers to use and evaluate homework, to hold administrators accountable for monitoring the homework load or to cultivate parents’ collaboration. Homework remains an orphan child of the educational excellence movement.
. . . After half a century of failure to increase student buy-in, it’s time to rethink how to make homework a more valued part of the pedagogic process. In addition to promoting academic achievement, homework can inculcate habits of self-discipline and independent study and can help inform parents about the educational agenda of their school. We must find ways to make homework an interesting and challenging educational experience for students, instead of the uniform, seat-bound, memorization-focused solo exercise it has been. Otherwise, all our talk about high standards and improving student achievement will run up against the same roadblock that has stymied the pursuit of educational excellence in the past.
SOURCE C
Tom Loveless, “Do Students Have Too Much Homework?” A report for the Brown Center on Education Policy at the Brookings Institution, Washington, D.C., 2003.
The following passage is excerpted from a report on American education.
The most reliable data support the following conclusions: 1) the typical student, even in high school, does not spend more than an hour per day on homework, 2) the homework load has not changed much since the 1980s, 3) the students whose homework has increased in the past decade are those who previously had no homework and now have a small amount, 4) most parents feel the homework load is about right and, of those who would like to change it, more parents would rather see homework increased than decreased.
. . . Research shows that the relationship of homework with student achievement is positive for both middle and high school students and neutral for elementary school students. The research does not prove causality, an ever-present difficulty with research on many educational practices. High-achieving students in high school, for example, may do more homework because they enjoy studying. They take tough classes that require a lot of work. That does not necessarily mean that homework is boosting their achievement. Low-achieving students in elementary school, on the other hand, may do more homework because they are struggling to catch up. The homework is not causing their learning problems.
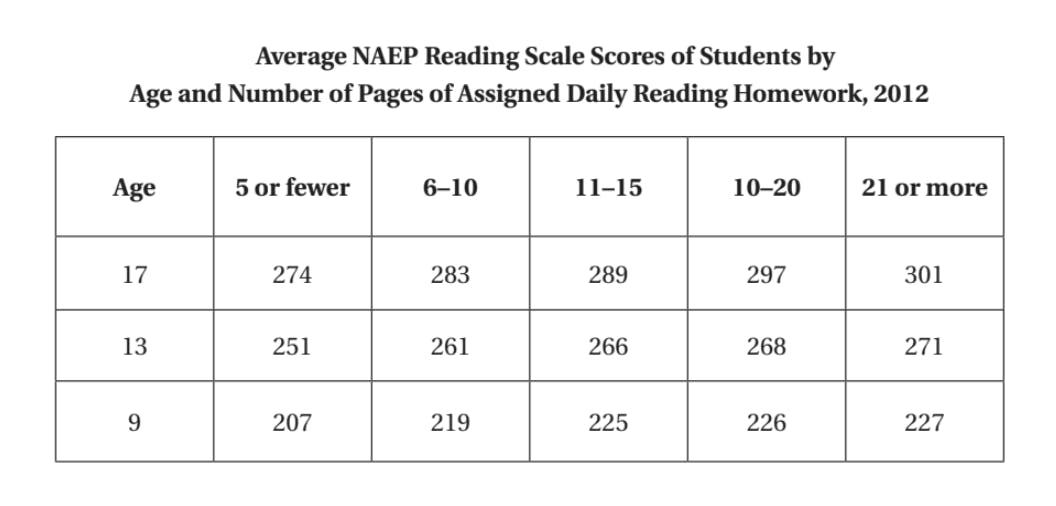
SOURCE D
“Average NAEP Reading Scale Scores of Students by Age and Amount of Assigned Daily Reading Homework,” Digest of Education Statistics, National Center for Educational Statistics, 2012.
See image below.
SOURCE E
Brian Haley, “What Is the Value of Homework?” July 6, 2006. SearchWarp.com. Accessed August 2, 2006, http://www.searchwarp.com
The passage that follows is adapted from an article published by a website that promotes the writing of authors in many disciplines, including education.
Assigning homework serves various educational needs. It serves as an intellectual discipline, establishes study habits, eases time constraints on the amount of curricular material that can be covered in class, and supplements and reinforces work done in school. In addition, it fosters student initiative, independence, and responsibility, and brings home and school closer together.
. . . Like mowing the lawn or taking out the garbage, homework seems to be a fact of life. . . . But the value of homework extends beyond school. We know that good assignments, completed successfully, can help children develop wholesome habits and attitudes. . . . It can teach children to work independently, encourage self-discipline and responsibility (assignments provide some youngsters with their first chance to manage time and meet deadlines), and encourage a love of learning. . . . Homework can help parents learn about their children’s education and communicate both with their children and the schools.
Research in the last decade has begun to focus on the relationship between homework and student achievement and has greatly strengthened the case for homework. Although there are mixed findings about whether homework actually increases students’ academic achievement, many teachers and parents agree that homework develops students’ initiative and responsibility and fulfills the expectations of students, parents, and the public. Studies generally have found homework assignments to be most helpful if they are carefully planned by the teachers and have direct meaning to students.
SOURCE F
Gloria Chaika, “Help! Homework Is Wrecking My Home Life,” Education World, August 8, 2000.
The following passage is from an article for school administrators published in an online educational journal.
“Teachers should devote energy to creating homework that is stimulating and provocative rather than banal,” says Howard Gardner of the Harvard Graduate School of Education. “And parents or mentors should go shoulder-to-shoulder with youngsters, helping to motivate them, thinking of ways in which to help them without giving the answer, and being aware of the child’s special gifts and weaknesses.”
It sounds great, “but you need parent input for kids to perform, and with the increase in single-parent families, there’s no one at home to help,” veteran fifth-grade teacher Loretta Highfield told Education World.
“It isn’t that the kids don’t want to do homework; the majority of my students don’t have the skills to go home and do it independently,” added Highfield, a teacher at Florida Avenue Elementary in Slidell, Louisiana. “Even young students are not getting the help at home that they used to.”
The same seems to hold true for older children. “I have students who have been thrown out of the house or have a financial situation brought on by an ill parent,” Northshore High School (Slidell, Louisiana) teacher Kathleen Modenbach told Education World. “There are others whose after-school jobs pay for car insurance and clothes or whose involvement in extra-curricular activities, private lessons, or sports leaves little time for homework.”
“For some students, a lot of homework can seem irrelevant,” Modenbach added. “High school students become expert at evaluating the validity of assignments and assigning priorities to them. Kids who wouldn’t dream of cheating on a test or copying a research paper think nothing of copying homework. I find students will do homework when it must be done to pass the class. Anything else is a waste of time and feeds into the vicious circle of beating the homework system.”
Therefore, as kids deal with assigned homework in their own ways—or grow increasingly frazzled—their too-busy parents are uncertain what to do. Some, wanting their children to be academically competitive, demand extra homework, while others wonder just how much is too much.
SOURCE G
Michael Hanson, “Analyzing ‘the Homework Gap’ Among High School Students,” Brown Center on Education Policy, 2017.
Researchers have struggled for decades to identify a causal, or even a correctional, relationship between time spent in school and improved learning outcomes for students. Some studies have focused on the length of the school year while others have focused on hours in a day or week, and others on hours spent on homework.
Measuring the relationship between homework and outcomes like test scores can be difficult. Researchers are primarily confounded by an inability to determine what compels students to choose homework during their time off over other activities. Are those who spend more time on homework just extra motivated? Or are they struggling students who need to work harder to keep up? What role do social expectations from parents and peers play?
Previous studies have examined the impact of this outside time use on educational outcomes for students. A recent study from Berea College in Kentucky identified a causal relationship between hours spent studying and a student’s academic performance through an interesting measure. The researchers took advantage of randomly assigned college roommates, paying attention to those who came to campus with smart phones packed with video games. They hypothesized students randomly assigned to a roommate without much interest in video games would study more, since all other factors remained equal. That hypothesis held up, and that group also received higher grades, demonstrating a causal relationship.
Other research has relied on data collected through the American Time Use Survey, a study of how Americans spend their time, and [has] shown the existence of a gender gap and a parental-education gap in homework time. Other studies have looked at the relationship between holding a job and students’ time use in discretionary activities, like sleep, media consumption, and time spent on homework.
SOURCE D (referenced above)
“Average NAEP Reading Scale Scores of Students by Age and Amount of Assigned Daily Reading Homework,” Digest of Education Statistics, National Center for Educational Statistics, 2012.
The table below has been adapted from research conducted by the National Association of Educational Progress, the nation’s largest testing agency responsible for assessing what America’s K–12 students know and can do in various subjects.
How to Answer the Synthesis Essay Question
Homework. Now, there’s a topic that you must know something about. Being a seasoned doer of homework, you’re probably bursting with ideas on the pros and cons of the stuff and could probably argue brilliantly for or against homework, or come down somewhere between the two poles. Regardless of where you stand, you’re not apt to find yourself short of ideas on the issue. In fact, you may be overloaded and find yourself sifting out only the best arguments among many to include in an essay on the subject.
But beware. This essay assignment is not intended simply to give you a chance to vent about homework. Although your biases will no doubt shape your argument, you mustn’t rely solely on your personal experience and observations. This, after all, is what the AP people call a “synthesis essay,” a label that you’ve got to take seriously.
AP English Language and Composition Synthesis Essay Step #1: Cite Sources
Stylistically, it may serve you well to use phrases like “According to Source C, . . .” or “In Loveless’s opinion . . .”, or “A study of students’ reading scores (Source D) shows that . . . ,” etc. Or you can simply cite your sources with parenthetical references—(Source A, Source B)—in your text. Another approach is to name the author or even the title of the sources, but writing out lengthy titles uses up precious time. AP essay readers will look for citations and will penalize essays that contain fewer than three. At the same time, however, you won’t earn extra credit for citing more than three.
Whether or not you agree with the premise that “large amounts of homework have more negative effects than positive ones,” your task is to write an argument that defends your point of view. Because a researched argument is meant to sway readers whose views may be contrary to yours, you need to gather compelling evidence in support of your position.
Let’s say that you think homework is generally good for you and the more you get, the better. Right off the bat, then, you have a main idea, or thesis, for your essay. But even if you know immediately where you stand on the issue, take the time to read all the sources carefully, underscoring or circling those ideas you might consider mentioning in your essay. It’s good to read the material with which you don’t agree, too, because in making your case, you can bolster your argument by refuting and revealing the weaknesses in what you’d expect your opponent to say.
AP English Language and Composition Synthesis Essay Step #2: Support Your Position
In building a convincing case, it often pays to gather at least three compelling reasons to support your position. Although AP students ought not be constrained by the familiar “five-paragraph” essay, you won’t go wrong following its structure: an introduction, three paragraphs of development, and a conclusion. Why three paragraphs of development? Mainly because three is a number that works. If you can come up with three different arguments, you appear to speak with the voice of authority. One paragraph is too simple. Two is better but still shallow. Three is thoughtful. It suggests depth and insight. Psychologically, three also creates a sense of wholeness for the reader, like the beginning, middle, and end of a story. (Incidentally, it’s no accident that the number three recurs in all literature, from Goldilocks and the Three Bears to the Bible.) Use the sources to bolster your arguments for or against large amounts of homework. But you needn’t depend totally on the sources. In fact, AP readers are likely to look kindly on your own original ideas, provided they are relevant to the issue, clearly expressed, and well- developed. On the positive side, you might pick out such ideas as:
- Homework permits parents to participate with teachers in the education of their children. (Source B)
- “[T]he relationship between the amount of reading homework and performance on reading tests is especially positive for high school students.” (Source D)
- Homework fosters the development of individual initiative and effective study habits. (Source B)
- Homework provides opportunities for low-achieving students to catch up. (Source C)
- Homework leads to a lifelong love of learning. (Source F)
- Homework generally contributes to higher grades, and higher grades can lead to admission to higher-quality colleges. (Source G)
Or, if you have an unfavorable view of homework, the following ideas can be used to support your argument:
- Years of educational research have found only a weak correlation between homework and student achievement. (Source A)
- Large amounts of homework can keep a student from pursuing worthwhile personal interests. (Source C)
- Homework assigned during vacations is counterproductive; it turns kids away from the joys of learning and deprives them of reading for pleasure. (Source E)
- More homework does not necessarily lead to better grades. (Source E)
The given sources either support or decry homework. A middle-of-the-road position may be difficult to defend unless you build a case by refuting arguments presented on both sides of the issue. Source F, which argues against homework, for example, quotes an apparently frustrated teacher: “It isn’t that kids don’t want to do homework; the majority of my students don’t have the skills to go home and do it independently.”
Because the word “majority” can mean almost all or just over half, the teacher appears to have overlooked the fact that some students can be counted on to work on their own. By generalizing about all students, the teacher in effect deprives some of her kids the opportunity to learn at home. An essay that argues neither for nor against homework might emphasize that universal policies regarding homework don’t work. In other words, when it comes to education, one size cannot fit all.
AP English Language and Composition Synthesis Essay Step #3: Determine Order
Once you’ve collected your ideas for or against the issue, stop for a moment to figure out which idea to put first, which to put second, and so on. Order is important. The best order is the clearest order, the arrangement that readers can follow with the least effort. No plan is superior to another, provided you have a valid reason for using it. The plan least likely to succeed is the aimless one, the one in which you state and develop ideas in random order as they happened to come to mind. It’s better by far to rank your ideas in order of importance by deciding which provides the strongest support for your thesis. Although your best argument may be listed first in your notes, save it for last on the essay. Giving it away at the start is self- defeating because everything that follows will be anticlimactic. An excellent way to arrange your ideas is to lead with your second best, save your best for the end, and sandwich the others in between. This structure recognizes that the end and the beginning of an essay are its most critical parts. A good opening draws the reader in and creates an all-important first impression, but a memorable ending, coming last, is what readers have fresh in their minds when they assign you a grade. But, as always, don’t just follow these guidelines slavishly. If you can justify another organization, by all means use it.
AP exam readers won’t judge your essay based on the opinion you express. Even if they disagree with you, they are obliged to ignore their own biases and grade you according to the criteria of good writing. They may think that your view is off the wall, but a cogent, forceful essay that smoothly integrates the sources and demonstrates mastery of argumentation will merit a high score.
Answering the AP English Language and Composition Rhetorical Analysis Essay Question
Sample Rhetorical Analysis Question
SUGGESTED TIME: 40 MINUTES
Read the following passage published back in 1967 by The New York Times. Then write an essay in which you analyze how the structure of the passage and the use of language help convey the writer’s views.
Instructions:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that may establish a line of reasoning.
- Select and use evidence to develop and support the line of reasoning.
- Explain the relationship between the evidence and the thesis.
- Demonstrate an understanding of the rhetorical situation.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating the argument.
Rhetorical Analysis Passage
Americans and Western Europeans, in their sensitivity to lingering problems around them, tend to make science and progress their scapegoats. There is a belief that progress has precipitated widespread unhappiness, anxieties, and other social and emotional problems. Science is viewed as a cold mechanical discipline having nothing to do with human warmth and the human spirit.
But to many of us from the nonscientific East, science does not have such repugnant associations. We are not afraid of it, nor are we disappointed by it. We know all too painfully that our social and emotional problems festered long before the age of technology. To us, science is warm and reassuring. It promises hope. It is helping us at long last gain some control over our persecutory environments, alleviating age-old problems—not only physical but also, and especially, problems of the spirit.
Shiraz, for example, a city in southern Iran, has long been renowned for its rose gardens and nightingales; its poets, Sadi and Hafiz; and its mystical, ascetic philosophy, Sufism. Much poetry has been written in glorification of the spiritual attributes of this oasis city. And to be sure, Shiraz is a green, picturesque town, with a quaint bazaar and refreshing gardens. But in this “romantic” city thousands of emotionally disturbed and mentally retarded men, women, and children were, until recently, kept in chains in stifling prison cells and lunatic asylums.
Every now and again, some were dragged, screaming and pleading, to a courtyard and flogged for not behaving “normally.” But for the most part, they were made to sit against damp walls, their hands and feet locked in chains, and thus immobilized, without even a modicum of affection from their helpless families and friends, they sat for weeks and months and years—often all their lives. Pictures of these wretched men, women, and children can still be seen in this “city of poetry,” this “city with a spiritual way of life.”
It was only recently that a wealthy young Shirazi who, against the admonitions of his family, had studied psychology at the University of Teheran and foreign universities, returned to Shiraz and after considerable struggle with city officials succeeded in opening a psychiatric clinic, the first in those regions. After still more struggle, he arranged to have the emotionally disturbed and the mentally retarded transferred from prison to their homes, to hospitals, and to his clinic, where he and his staff now attend them.
They are fortunate. All over Asia and other backward areas, emotionally disturbed men and women are still incarcerated in these medieval dungeons called lunatic asylums. The cruel rejection and punishment are intended to teach them a lesson or help exorcise evil spirits.
The West, still bogged down in its ridiculous romanticism, would like to believe that emotional disturbances, dope addiction, delinquency are all modern problems brought on by technological progress, and that backward societies are too spiritual and beautiful to need the ministrations of science. But while the West can perhaps afford to think this way, the people of backward lands cannot. . . .
. . .The obstacles are awesome, the inertia too entrenched, the people’s suffering too anguished, their impatience too eruptive. Moreover, the total cultural reorganizations such as Asia and Africa are undergoing inevitably engender their own temporary dislocations and confusions. But their goals, the direction, remain constant. We are on the move, however awkwardly at first, to a saner, better world.
How to Answer the Rhetorical Analysis Question
Go back to the original question, which asks you to analyze two features of the passage: (1) its structure, or organization, and (2) its language. The first aspect is fairly specific. As you read the passage, you need to observe what the author discusses first, second, third, and so on. Your essay should explain not only the order of ideas but the reasons the author may have chosen that order.
The second part of the question is more general. It invites you to analyze the use of language, which may include the author’s choice of words (diction), syntax (word order), figures of speech, use of evidence (such as statistics or logical reasoning), sentence structure, rhythm, sound, tone, or just about any other characteristics of style and rhetoric you choose.
Although the question directs you to write about two different aspects of the passage, the essay itself should be unified. That is, a good essay should not consist of, say, two disparate paragraphs, one exclusively devoted to structure and another to language. Rather, the essay should include material that shows the interrelationship of structure and language in the passage and how those elements contribute to the meaning and effect of the passage. This might be covered in a separate paragraph, or it could be woven into the overall fabric of the essay.
Before you begin to write, read the passage at least twice: once for an overview and once as you write your analysis. You may notice early on that the opening paragraph contains generalizations about Westerners’ concepts of science and progress. Then the author contrasts the Western view of science and progress with the Eastern view. Immediately, you see that the author, by using the first-person pronoun (as in “many of us”) is speaking from the perspective of an Easterner. Consequently, his discussion of Eastern views is apt to come across as more well-informed, more authoritative, perhaps more personal.
To support his position, the author gives an extended example—the city of Shiraz—to illustrate just how different the East is from the West. The description and vivid images of Shiraz memorably convey the idea that the “spiritual way of life” has a side to it that many Westerners don’t know about. This is the heart of the passage. The use of quotation marks around “romantic” and “city of poetry” is meant to point out the discrepancy between the idealized and real versions of Shiraz.
Nearing the end, the author reiterates his initial contrast between West and East, with emphasis on the East. The last paragraph offers a generalized statement about conditions in Asia and Africa, reminding the reader of the contrast made at the very beginning of the passage. Tying the end to the beginning of the passage creates a sense of unity—a desirable feature in any piece of writing.
Answering the AP English Language and Composition Argument Essay Question
The third essay on the exam requires you to respond to an idea contained in a short statement or paragraph. Your response must be written as an argument that either supports or refutes a writer’s views on a particular subject. Or, if you prefer not to take an either/or position, you can adopt a stance somewhere in between the two.
Writing a persuasive essay involves more than simply expressing your opinion on an issue. The validity of your position must be based on sound evidence. Passion alone won’t do it. You need to corral evidence from your experience, reading, studies, and observation in order to prove that your opinion has merit.
To argue on behalf of your position, find at least two (three is even better) distinct arguments to support it. It helps, too, to develop a counterargument—an argument most likely to be used by someone who opposes your views—that you can refute in order to persuade readers that you are right and your opponent is not.
Because topics for AP persuasive essays are unpredictable, it makes sense to arm yourself with a ready-to-use essay-writing strategy—one that, regardless of the topic, lays out the steps to take during the approximately forty minutes it takes to complete the essay. Chances are that you’ve written reams of essays during your school career. Over the years, you may have developed a method for writing blue-ribbon essays. But in case you haven’t, here is a list of steps you can count on. Follow them while you write essays for practice. Then, based on the results you get, amend the list in ways that enable you to write the best essays you can.
- Read and analyze the prompt.
- Jot down ideas that might be used to argue both sides of the issue.
- Review the ideas and choose a position on the issue.
- Articulate a main idea, or thesis, for your essay.
- Arrange supporting ideas purposefully—not simply in the order they occurred to you.
- Introduce the main idea of your essay.
- Develop unified paragraphs in support of your main idea.
- Devote at least part of your essay to refute an argument likely to be used by someone whose opinion differs from yours.
- Choose words and structure sentences that concisely convey your thoughts.
- Write a memorable conclusion but not a brief summary of your essay.
- Edit your essay for clarity, interest, and correctness.
Experience shows that these steps do not need be taken in the order presented, nor is each step discrete. Rather, they often overlap and blend into each other. While composing your essay, for example, you may also be revising and proofreading. Late in the process, you may weave new ideas into your text or shift the location of ideas. In short, no step really ends until the final period is put into place or the AP proctor calls “Time!” We can't tell you exactly how much of the suggested 40-minute writing period to devote to each step. A plan that works for other students may not work for you. In general, however, you won’t go wrong by devoting more than half the time—about 25–30 minutes—to composing an essay and no more than 5–10 minutes planning and polishing it. By now you may have noticed that the basic process of writing a persuasive essay hardly differs at all from that used in writing synthesis or analytical essays. All three require you to read the prompt over and over until you are absolutely sure of what it says and what you are expected to do. The prompt may not interest you right away, but if you really concentrate on the issue, you may soon be bursting with ideas for your essay.
Sample Argument Essay Question
SUGGESTED TIME: 40 MIINUTES
The following paragraph is adapted from Mirror for Man, a book written by anthropologist Clyde Kluckhorn in the middle of the twentieth century. Read the passage carefully. Then, write an essay that examines the extent to which the author’s characterization of the United States holds true today. Use appropriate evidence to support your argument.
Instructions:
- Respond to the prompt with a thesis that may establish a line of reasoning.
- Select and use evidence to develop and support the line of reasoning.
- Explain the relationship between the evidence and the thesis.
- Demonstrate an understanding of the rhetorical situation.
- Use appropriate grammar and punctuation in communicating the argument.
Technology is valued as the very basis of the capitalistic system. Possession of gad- gets is esteemed as a mark of success to the extent that persons are judged not by the integrity of their characters or by the originality of their minds but by what they seem to be—so far as can be measured by their wealth or by the variety and material goods which they display. “Success” is measured by their investments, homes, and lifestyles— not by their number of mistresses as in some cultures.
How to Answer the Argument Question
Whether you agree, disagree, or have mixed views on the content of the passage, your job is to write a convincing argument that expresses your opinion. Initially, the word argument may suggest conflict or confrontation. But rest assured that your essay need not be combative. Rather, make it a calmly-reasoned explanation of your opinion on a debatable subject. Your goal is to persuade the reader that your opinion, supported by examples, facts, and other appropriate evidence, is correct.
If you have strong feelings about the topic, of course you should state them in your essay. But express them in calm, rational language. Be mindful that the essay should not be an emotional rant for or against the issue.
Consider first whether you agree with Kluckhorn’s definition of “success.” Is it, as Kluckhorn asserts, measured by income and material possessions? Or do you think that a more accurate standard of success in today’s America should be determined by less tangible criteria—things such as happiness or self-respect? Or do you stand somewhere in between those two extremes?
The actual position you take on the issue is less crucial than your ability to support it fully by drawing from your knowledge, background, experience, or observation. Regardless of your position, be sure to include more than one example. An argument that relies on a single example, however compelling, will fall flat.
In the prompt, Kluckhorn’s notion of success seems to refer broadly to American society. Resist responding in kind. That is, a short essay shouldn’t focus on the whole of society but only on an identifiable segment—perhaps college-educated professionals or urban, blue-collar Americans. The point is that a narrowly focused essay on a limited topic will always turn out better than one that tries to cover too much ground in just a few paragraphs.
AP Biology Resources
- About the AP Biology Exam
- Top AP Biology Exam Strategies
- Top 5 Study Topics and Tips for the AP Biology Exam
- AP Biology Short Free-Response Questions
- AP Biology Long Free-Response Questions
AP Psychology Resources
- What’s Tested on the AP Psychology Exam?
- Top 5 Study Tips for the AP Psychology Exam
- AP Psychology Key Terms
- Top AP Psychology Exam Multiple-Choice Question Tips
- Top AP Psychology Exam Free Response Questions Tips
- AP Psychology Sample Free Response Question
AP English Language and Composition Resources
- What’s Tested on the AP English Language and Composition Exam?
- Top 5 Tips for the AP English Language and Composition Exam
- Top Reading Techniques for the AP English Language and Composition Exam
- How to Answer the AP English Language and Composition Essay Questions
- AP English Language and Composition Exam Sample Essay Questions
- AP English Language and Composition Exam Multiple-Choice Questions
